What Does It Mean if You Get Your Period One Time Then Never Again
Having no menstrual periods is called amenorrhea.
Amenorrhea is normal in the post-obit circumstances:
-
Before puberty
-
During pregnancy
-
While breastfeeding
-
Afterward menopause
At other times, it may be the outset symptom of a serious disorder.
Amenorrhea may be accompanied past other symptoms, depending on the cause. For example, women may develop masculine characteristics (virilization), such as excess body hair (hirsutism Hairiness In men, the amount of body hair varies profoundly (come across also Overview of Hair Growth), only very few men are concerned enough about excess hair to see a doctor. In women, the corporeality of hair that... read more 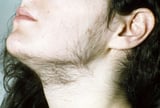 ), a deepened voice, and increased muscle size. They may have headaches, vision issues, or a decreased sexual practice bulldoze. They may have difficulty condign pregnant.
), a deepened voice, and increased muscle size. They may have headaches, vision issues, or a decreased sexual practice bulldoze. They may have difficulty condign pregnant.
In most women with amenorrhea, the ovaries do not release an egg. Such women cannot become pregnant.
If amenorrhea lasts a long time, problems similar to those associated with menopause Menopause Menopause is the permanent end of menstrual periods and thus of fertility. For up to several years earlier and simply after menopause, estrogen levels fluctuate widely, periods become irregular... read more  may develop. They include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, decreased bone density (osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition in which a decrease in the density of basic weakens the bones, making breaks (fractures) likely. Aging, estrogen deficiency, low vitamin D or calcium intake, and... read more
may develop. They include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, decreased bone density (osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a condition in which a decrease in the density of basic weakens the bones, making breaks (fractures) likely. Aging, estrogen deficiency, low vitamin D or calcium intake, and... read more  ), and an increased take a chance of heart and claret vessel disorders. Such problems occur because in women who have amenorrhea, the estrogen level is low.
), and an increased take a chance of heart and claret vessel disorders. Such problems occur because in women who have amenorrhea, the estrogen level is low.
In that location are ii main types of amenorrhea:
-
Main: Menstrual periods never beginning.
-
Secondary: Periods start, then stop.
Usually if periods never showtime, girls do not go through puberty, and thus secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts and pubic hair, do non develop ordinarily.
If women have been having menstrual periods, which then stop, they may have secondary amenorrhea. Secondary amenorrhea is much more common than primary.
-
The hypothalamus (part of the brain that helps control the pituitary gland)
-
The pituitary gland, which produces luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone
-
The ovaries, which produce estrogen and progesterone
Other hormones, such equally thyroid hormones and prolactin (produced by the pituitary gland), can bear upon the menstrual bike.
The most common reason for no menstrual periods in women who are non significant or breastfeeding is
-
Malfunction of any role of this hormonal arrangement
When this organisation malfunctions, the ovaries do not release an egg. The type of amenorrhea that results is called anovulatory amenorrhea.
Less commonly, the hormonal system is functioning normally, but some other trouble prevents periods from occurring. For case, menstrual bleeding may non occur because the uterus is scarred or considering a nascency defect, fibroid, or polyp blocks the catamenia of menstrual blood out of the vagina.
High levels of prolactin, which stimulates the breasts to produce milk, can result in no periods.
Amenorrhea can issue from weather condition that affect the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, uterus, cervix, or vagina. These conditions include hormonal disorders, nascence defects, genetic disorders, and drugs.
Which causes are most mutual depends on whether amenorrhea is primary or secondary.
The disorders that cause main amenorrhea are relatively uncommon, only the nearly mutual are
-
A genetic disorder
Genetic disorders include
-
Disorders that effect in having a Y chromosome (which normally occurs just in males).
Genetic disorders and nascence defects that cause primary amenorrhea may not be noticed until puberty. These disorders crusade only principal amenorrhea, non secondary.
Sometimes puberty is delayed in girls who practise non have a disorder, and normal periods simply brainstorm at a later age. Such delayed puberty may run in families.
The nigh common causes are
-
Pregnancy
-
Breastfeeding
-
Malfunction of the hypothalamus
-
Malfunction of the pituitary gland or the thyroid gland
-
Utilise of certain drugs, such as birth control pills (oral contraceptives), antidepressants, or antipsychotic drugs
Pregnancy is the virtually mutual crusade of amenorrhea among women of childbearing historic period.
The hypothalamus may malfunction for several reasons:
-
Stress or excessive exercise (as done by competitive athletes, peculiarly women who participate in sports that involve maintaining a low body weight)
-
Radiation therapy or an injury
The pituitary gland may malfunction because
-
It is damaged.
-
Levels of prolactin are high.
Antidepressants, antipsychotic drugs, oral contraceptives (sometimes), or certain other drugs can cause prolactin levels to increase, as tin pituitary tumors and some other disorders.
Less common causes of secondary amenorrhea include chronic disorders (specially of the lungs, digestive tract, claret, kidneys, or liver), some autoimmune disorders, cancer, HIV infection, radiation therapy, caput injuries, a hydatidiform mole (overgrowth of tissue from the placenta), Cushing syndrome, and malfunction of the adrenal glands. Scarring of the uterus (usually due to an infection or surgery), polyps, and fibroids can likewise cause secondary amenorrhea.
Doctors determine whether amenorrhea is primary or secondary. This information can aid them identify the cause.
Certain symptoms are crusade for concern:
-
Delayed puberty
-
Development of masculine characteristics, such equally excess body hair, a deepened vocalism, and increased muscle size
-
Vision bug
-
A pregnant change in weight
Girls should see a doctor within a few weeks if
-
They take no signs of puberty (such equally breast development or a growth spurt) by age xiii.
-
Periods have not started by age 15 in girls who are growing normally and take adult secondary sexual characteristics.
Such girls may take primary amenorrhea.
If girls or women of childbearing age have had menstrual periods that have stopped, they should see a doctor if they have
-
Missed 3 menstrual periods
-
Fewer than 9 periods a yr
-
A sudden change in the design of periods
Such women may accept secondary amenorrhea. Doctors always do a pregnancy test when they evaluate women for secondary amenorrhea. Women may wish to do a home pregnancy test before they run into the doctor.
Doctors beginning ask almost the medical history, including the menstrual history. Doctors then exercise a physical examination. What they find during the history and physical examination often suggests a cause of amenorrhea and the tests that may need to be done (encounter table Some Causes and Features of Amenorrhea Some Causes and Features of Amenorrhea ![]() ).
).
For the menstrual history, doctors decide whether amenorrhea is primary or secondary past asking the girl or woman whether she has ever had a menstrual flow. If she has, she is asked how old she was when the periods started and when the last period occurred. She is also asked to describe the periods:
-
How long they lasted
-
How ofttimes they occurred
-
Whether they were ever regular
-
How heavy they were
-
Whether her breasts were tender or she had mood changes related to periods
If a daughter has never had a menses, doctors ask
-
Whether breasts take started to develop
-
Whether she has had a growth spurt
-
Whether pubic and underarm hair (signs of puberty) has appeared
-
Whether whatever other family fellow member has had abnormal periods
This information enables doctors to rule out some causes. Information almost delayed puberty and genetic disorders in family members tin can help doctors decide whether the cause is a genetic disorder.
Doctors enquire well-nigh other symptoms that may suggest a cause and about use of drugs, practice, eating habits, and other weather condition that tin cause amenorrhea.
During the physical examination, doctors determine whether secondary sexual characteristics have developed. A chest examination is washed. A pelvic test is done to determine whether genital organs are developing normally and to check for abnormalities in reproductive organs.
Doctors also check for symptoms that may advise a cause such every bit
-
A milky belch from both nipples: Possible causes include pituitary disorders and drugs that increment levels of prolactin (a hormone that stimulates milk product).
-
Headaches, hearing loss, and partial loss of vision or double vision: Possible causes include tumors of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
-
Development of masculine characteristics, such as excess torso hair, a deepened vocalism, and increased muscle size: Possible causes include polycystic ovary syndrome, tumors that produce male person hormones, and utilise of drugs such as synthetic male hormones (androgens), antidepressants, or loftier doses of constructed female person hormones chosen progestins.
-
Hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and dark sweats: Possible causes include premature menopause, a disorder that causes the ovaries to malfunction, radiation therapy, and use of a chemotherapy drug.
-
Shakiness (tremors) with weight loss or sluggishness with weight proceeds: These symptoms suggest a thyroid disorder.
In girls or women of childbearing age, the get-go examination is
-
A pregnancy exam
If pregnancy is ruled out, other tests are done based on results of the examination and the suspected crusade.
If girls have never had a period (primary amenorrhea) and have normal secondary sexual characteristics, testing begins with ultrasonography to check for birth defects that could cake menstrual claret from leaving the uterus. If nascence defects are unusual or difficult to place, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be done.
Tests are usually washed in a certain lodge, and causes are identified or eliminated in the process. Whether additional tests are needed and which tests are done depend on results of the previous tests. Typical tests include
-
Blood tests to mensurate levels of prolactin (to bank check for atmospheric condition that cause loftier levels), thyroid hormones (to check for thyroid disorders), follicle-stimulating hormone (to check for pituitary or hypothalamus malfunction), and male hormones (to check for disorders that cause masculine characteristics to develop)
-
Imaging tests of the belly and pelvis using computed tomography (CT), MRI, or ultrasonography to look for a tumor in the ovaries or adrenal glands
-
Examination of chromosomes in a sample of tissue (such as blood) to bank check for genetic disorders
-
Use of hormones (estrogen and a progestin or progesterone) to try and trigger menstrual bleeding
For hysteroscopy, doctors insert a thin viewing tube through the vagina and cervix to view the interior of the uterus. This procedure can be washed in a physician's office or in a hospital equally an outpatient procedure.
For hysterosalpingography, ten-rays are taken afterward a substance that tin can exist seen on x-rays (a radiopaque dissimilarity agent) is injected through the cervix into the uterus and fallopian tubes. Hysterosalpingography is usually done as an outpatient procedure in a hospital radiology suite.
If hormones trigger menstrual bleeding, the crusade may be malfunction of the hormonal system that controls menstrual periods or premature menopause. If hormones practice not trigger bleeding, the cause may be a disorder of the uterus or a structural abnormality preventing menstrual claret from flowing out.
If symptoms suggest a specific disorder, tests for that disorder may be done first. For example, if women have headaches and vision problems, MRI of the brain is done to check for a pituitary tumor.
When amenorrhea results from another disorder, that disorder is treated if possible. With such treatment, menstrual periods sometimes resume. For example, if an aberration is blocking the flow of menstrual blood, it is usually surgically repaired, and periods resume. Some disorders, such equally Turner syndrome and other genetic disorders, cannot be cured.
If women accept a Y chromosome, doctors recommend surgical removal of both ovaries considering having a Y chromosome increases the risk of ovarian germ cell cancer Ovarian Cancer . Ovarian germ cell cancer starts in the cells that produce eggs (germ cells) in the ovaries.
If a daughter's periods never started and all exam results are normal, she is examined every 3 to 6 months to cheque on the progression of puberty. She may be given a progestin and sometimes estrogen to start her periods and to stimulate the development of secondary sexual characteristics, such as breasts.
Problems associated with amenorrhea may crave treatment, such as
-
Treating symptoms and long-term effects of an estrogen deficiency (for example, by taking vitamin D, consuming more calcium in the diet or in supplements, or taking drugs, including hormone therapy and drugs that prevent bone loss such as bisphosphonates Drugs
 or denosumab for fractures caused past osteoporosis)
or denosumab for fractures caused past osteoporosis)
-
Various conditions can disrupt the complex hormonal system that regulates the menstrual cycle, causing menstrual periods to terminate.
-
Doctors distinguish between primary amenorrhea (periods have never started) and secondary amenorrhea (periods started, then stopped).
-
The first test is a pregnancy test.
-
Unless a woman is pregnant, other testing is ordinarily required to determine the cause of amenorrhea.
-
Issues related to amenorrhea (such as a low estrogen level) may also require treatment to preclude afterward health problems.
hodgkinsonforit1992.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/women-s-health-issues/menstrual-disorders-and-abnormal-vaginal-bleeding/absence-of-menstrual-periods
0 Response to "What Does It Mean if You Get Your Period One Time Then Never Again"
Post a Comment